Did you know that almost half of Americans consume less magnesium than their body needs? Subclinical magnesium deficiency is easy to miss – but its consequences can be serious. Your body’s lack of magnesium can contribute to both physical and psychiatric symptoms such as muscle spasms, cramps, anxiety, and depression. In severe cases, it can also contribute to osteoporosis, high blood pressure, and even coronary heart disease. To achieve optimal health and prevent disease, you need to ensure that you are getting enough magnesium.
Read on for everything you need to know about plant-based magnesium and why you should consider a magnesium supplement.
The Dangers of Sub-Clinical Magnesium Deficiency
According to multiple surveys, many North Americans ingest less magnesium than their Estimated Average Requirement (EAR). According to data collected by the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2013-2016, 48% of all Americans ingest less magnesium than they should. Adult men who were over 70 years old and adolescent males and females were most likely to consume insufficient amounts of magnesium.
Recent studies in Germany, France, Taiwan, Japan, and Ukraine also discovered inadequate magnesium intake across a broad swath of demographics.
Unfortunately, magnesium deficiency often goes unnoticed because it is typically subclinical. This means that its symptoms are less obvious and may be attributed to other causes. They are a “clinically silent reduction in physiological, cellular, and/or biochemical functions.”
Because it is harder to diagnose, a subclinical deficiency can go undiagnosed and untreated until symptoms worsen significantly.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency
A person’s symptoms will vary depending on the severity of the magnesium deficiency. Less severe symptoms may include the following:
General symptoms:
- Cramps (particularly in hands and feet)
- Muscular weakness
- Neuromuscular irritability
- Pain or hyperalgesia
- Muscle spasms (tetany) or tightness (spasticity)
- Tremors
Psychiatric/Emotional symptoms:
- Aggression
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Hallucinations
Neurological symptoms:
- Confusion
- Fasciculations (flickers of movement under the skin, caused by a motor neuron disease)
- DisorientationM
- Vertigo
- Ataxia (lack of muscle coordination)
- Chvostek sign (twitching of the facial muscles in response to tapping over the area of the facial nerve)
- Tinnitus
In more severe cases, the symptoms can include the following:
- Arrhythmias (irregular heartbeat), tachycardia (increased heart rate), and other heart problems
- Cataracts
- Convulsions
- Coronary artery disease
- Depression
- Hearing loss
- High blood pressure
- Headaches and migraines
- Osteoporosis
- Psychotic behavior
- Seizures
- Sudden cardiac failure
Clearly, magnesium plays a critical role in keeping your body functioning in a healthy manner. Next, we’ll look at why your body needs magnesium.
Why The Body Needs Magnesium
First, magnesium is the fourth most plentiful cation in the human body. It participates in over 300 enzyme systems of the body that regulate everything from blood glucose to protein synthesis. Here are just a few of the many functions of magnesium in your body.
- Strengthens bones and works with bone-building cells to produce new bone matter
- Required for the production of DNA, RNA, and glutathione
- Helps transport calcium and potassium ions across cell membranes (which is necessary for heart rhythm and muscle contractions)
- Enables your body to unlock and burn energy from blood glucose
- Helps regulate blood pressure
How Your Body Regulates Magnesium Levels
On average, each human body contains about 24 grams of magnesium. About 50-60% of the body’s magnesium is stored in bones, while the rest is scattered throughout the soft tissues of the body.
Blood serum holds less than 1% of the body’s magnesium, and that level is strictly regulated by the kidneys.
Magnesium levels are regulated by three central processes: absorption via the gut, exchange with magnesium reserves stored in bone, and kidney filtration, excretion, and reabsorption.
Interestingly enough, the gut can absorb anywhere from 25-75% of magnesium consumed in the diet. This number depends on a variety of factors, including whether the body is deficient in magnesium.
When magnesium levels are dangerously low, the body can draw magnesium out from muscle and bones. While this provides readily available magnesium, it also can cause magnesium deficits. This is why magnesium deficiency can lead to diseases such as osteoporosis. It can also increase the risk of bone fractures and cause a loss in bone density over time.
On average, the kidneys filter about 2.4 grams of magnesium per day. They reabsorb about 95% of it and excrete the excess magnesium via the urine. If magnesium levels are low, they retain more magnesium to compensate. If magnesium levels are high, the kidneys excrete more magnesium.
This is why doctors often measure magnesium levels via urinary magnesium levels. A level less than 80 mg/d can suggest a possible magnesium deficiency.
What Causes A Magnesium Deficiency?
Multiple factors – both temporary and permanent – can intersect to cause a magnesium deficiency.
First, some people have inadequate dietary intake. Curiously, scientific studies have noted that micronutrient levels in some foods have declined since the 1950s. For example, the magnesium content of modern wheat is almost 20% lower than it was in the 1960s, potentially due to soil changes and modern farming methods.
Magnesium has also dropped 24% in vegetables, 21% in whole milk, 38% in cheddar cheese, and a whopping 70% in Parmesan cheese. It has even dropped 4-8% in beef and 4% in chicken. In our day, it’s become much harder to gain adequate magnesium through diet alone. That’s why many people have turned to magnesium supplements.
Natural Supplements Are Ideal For Magnesium Deficiency
What is the best source of magnesium? Because diet is often inadequate to meet your magnesium requirements, we recommend magnesium supplementation. If you suspect that you may have a magnesium deficiency, it’s not too late to start providing your body with the nutrients it desperately needs. With the right magnesium supplement, you can achieve optimal health.
Our E-Z Mg is a plant-based magnesium supplement formulated from organic Swiss chard and buckwheat. They are grown on a sustainable, certified organic farm in Wisconsin. Because this magnesium is plant-based, it contains multiple forms of magnesium, which reduces the risk of gastrointestinal side effects. It’s easy to absorb the way nature intended.
The recommended dosage of E-Z Mg is six capsules daily, or 70 mg of elemental magnesium. This amount is sufficient for the dietary needs of about 70% of the population. The remaining 30% of the population, with extremely low magnesium levels, should increase their intake of plant-based foods containing magnesium in addition to consuming E-Z Mg.
E-Z Mg is designed to support patients with inadequate dietary magnesium intake. It helps to bridge the gap in dietary magnesium intake. By ensuring that your magnesium levels are healthy, you can avoid preventable, serious health issues such as osteoporosis, heart problems, and more.
Health Benefits Of Magnesium Intake
Beyond preventing certain illnesses, magnesium also provides some amazing health benefits.
First, magnesium reduces stress. During the Covid-19 pandemic, stress levels around the world have surged as people grappled with fear, health risks, unemployment, and other challenges. In these challenging times, we could all benefit from reduced stress levels.
A study in France followed 242 people who suffered from psychological stress. The patients were given a regimen of magnesium supplements, vitamins, and probiotics. Within a month, the patients’ stress and fatigue symptoms had both decreased significantly.
Another study involved 126 adults with mild to moderate depression. They supplemented with magnesium for six weeks. After this period, anxiety scores and depressive symptoms improved dramatically. Over half of the participants said they would continue to supplement with magnesium.
Second, higher magnesium intake reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. This may be due to the important role that magnesium plays in blood glucose metabolism. Low magnesium levels have been linked to insulin resistance, which is a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Diabetes also leads to increased loss of magnesium via urine, which exacerbates the situation.
Magnesium supplementation can cut the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 15-17%, according to one study. Another study showed that risk decreased by 8-13% for every 100 mg of magnesium consumed daily.
How Much Magnesium Should You Take?
Your magnesium needs depend on your age, gender, and overall health profile. To get the most accurate recommendation, consult with your family physician.
Here is a list of recommended daily allowances (RDAs) and estimated average requirements (EARs) for different age groups.
- Females ages 19-30—EAR: 255 mg/day and RDA: 310 mg/day
- Males ages 19-30—EAR: 330 mg/day and RDA: 400 mg/day
- Females over age 30—EAR: 265 mg/day and RDA: 320 mg/day
- Males over age 30—EAR: 350 mg/day and RDA: 420 mg/day
- Pregnant females ages 19-20—EAR: 290 mg/day and RDA: 350 mg/day
- Pregnant females ages 31-50—EAR: 300 mg/day and RDA: 360 mg/day
Generally speaking, pregnant females and males need more magnesium than other groups. However, people of all ages and demographics often have an undiagnosed magnesium deficiency. This is why supplementation is so important.
How Does Plant-Based Magnesium Compare To Other Magnesium Supplements?
Magnesium is available in several different forms. One of the most common formulations is magnesium citrate, which is magnesium bound with citric acid (this occurs naturally in citrus fruits). This type is taken orally and is easy to absorb but can also have a laxative effect.
Another form, magnesium lactate, is the salt produced by lactic acid plus magnesium. It’s commonly used as a food additive to fortify foods and regulate acid levels. It is typically easier to digest than other forms.
Magnesium taurate is produced using the amino acid taurine, which may help with blood sugar levels and blood pressure regulation. More study is needed to confirm these benefits.
Magnesium glycinate is made up of the amino acid glycine and elemental magnesium. (Glycine is an amino acid that your body uses for protein synthesis.) This supplement is often used to treat sleep problems, anxiety, and depression. However, scientific evidence of its benefits is limited.
Magnesium orotate is made with orotic acid, which your body uses to produce genetic material such as DNA. It’s easily absorbed and may improve heart health. It’s popular among competitive athletes but can also help heart patients. However, this form is much more expensive than other magnesium supplements.
NOTE: Magnesium supplements can also interact with several common medications. If you are taking daily medications, you should take magnesium at least two or more hours apart from your other medications. If you have kidney disease, you should not take magnesium without the supervision of a physician.
Unfortunately, many magnesium supplements have side effects. The most common include an upset stomach, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
However, plant-based magnesium is much easier to absorb and digest than other forms. Because it contains multiple forms of magnesium – instead of just one or two – it is significantly easier for the body to digest.
E-Z Mg contains exclusively plant-based magnesium, which is a collection of various magnesium forms. Because of this natural variety, it is not expected to have the same gastrointestinal side effects as other types of magnesium.
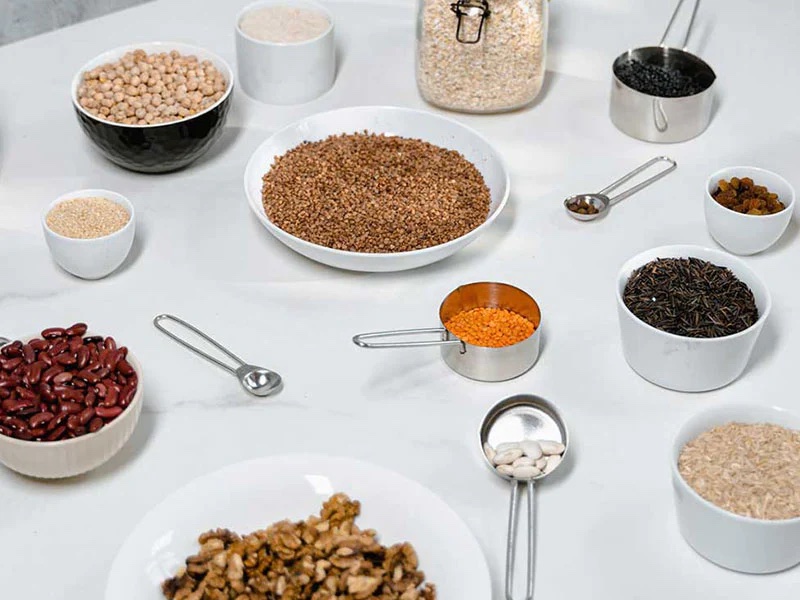
Plant-Based Foods To Boost Magnesium Levels
If you want to increase your magnesium levels, plant-based foods are an excellent choice. Magnesium is commonly found in legumes, dark green leafy vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and seeds. Here are some specific foods to include in your diet for more magnesium.
- Peanut butter
- Pumpkin seeds
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Black or kidney beans
- Cooked spinach and Swiss chard
- Brown rice
- Oatmeal
- Banana
- Dark chocolate!
Unfortunately, since foods have changed so much over the last half-century, their micronutrient content has decreased significantly. That’s why we recommend supplementing with magnesium daily.
Our E-Z Mg is an organic, easy to absorb magnesium supplement formulated from organic Swiss chard and buckwheat. It provides enough magnesium for most people to achieve healthy magnesium levels and enjoy optimal health.
Whole Body Solutions has been helping individuals safeguard their health through safe and natural means for over 30 years.
The center was founded by Dr. Ann Doggett, an accomplished chiropractor and nutritionist. Her credentials include:
- Doctorate of Chiropractic (New York Chiropractic College, 1989)
- Master’s Degree in Human Nutrition (University of Bridgeport, 2000)
- Advanced Clinical Training in Nutrition Response Testing (Ulan Nutritional Systems, 2006)
- Certification in Practical Herbal Therapy (Australian College of Phytotherapy, 2008)
Our services include nutrition, chiropractic, acupuncture, weight management, and brain integration to help clients achieve wellness. We take a big-picture approach to their health and wellness concerns. Dr. Doggett has had great success treating back pain, chronic fatigue, stress anxiety, ADD/ADHD, infertility, weight loss, and digestive disorders, just to name a few.
You can reach Whole Body Solutions here. You can also contact the center at 617.328.6300 and [email protected]. We can’t wait to be part of your wellness journey.


 Opened more than 30-years ago by Dr. Ann Doggett, WholeBody Solutions is a holistic wellness center whose mission is to provide the community with safe, effective, and natural answers to health and wellness concerns. Our all-encompassing wellness center focuses on the following drug-free services: Nutrition, Chiropractic, Acupuncture, and Weight Loss. Our goal is quite simple – to make sick people well and to keep healthy people healthy. It’s that simple and that powerful.
Opened more than 30-years ago by Dr. Ann Doggett, WholeBody Solutions is a holistic wellness center whose mission is to provide the community with safe, effective, and natural answers to health and wellness concerns. Our all-encompassing wellness center focuses on the following drug-free services: Nutrition, Chiropractic, Acupuncture, and Weight Loss. Our goal is quite simple – to make sick people well and to keep healthy people healthy. It’s that simple and that powerful.